Understanding the Coffee Flavor Wheel: Essential Guide to Specialty Coffee Culture and 2023 SCAA Coffee Flavor Wheel HD Chart
Professional coffee knowledge exchange. For more coffee bean information, please follow Coffee Workshop (WeChat public account: cafe_style).
For more specialty coffee beans, please add FrontStreet Coffee's private WeChat account: qjcoffeex
Latest Chinese and English Versions of Coffee Flavor Wheel
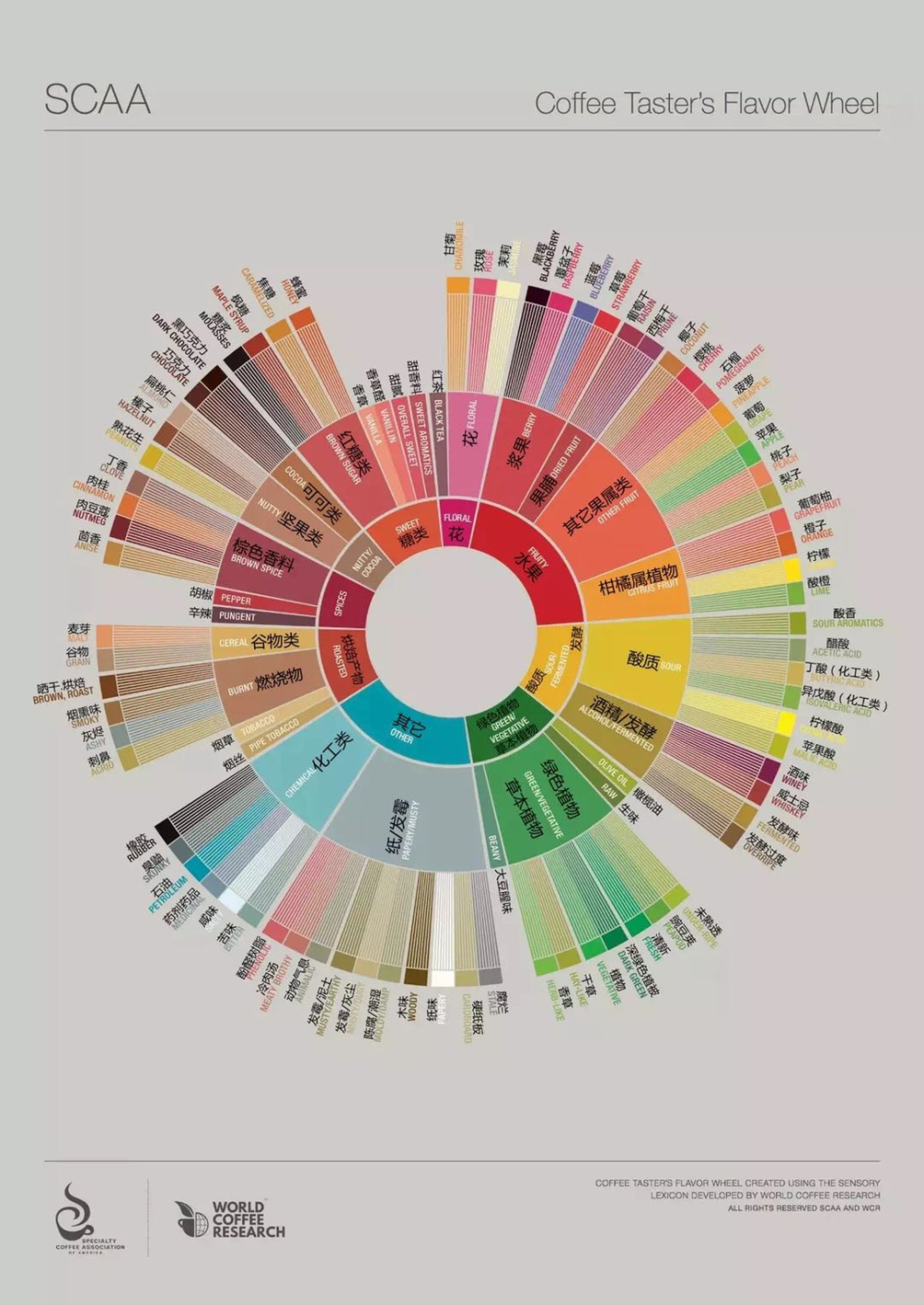
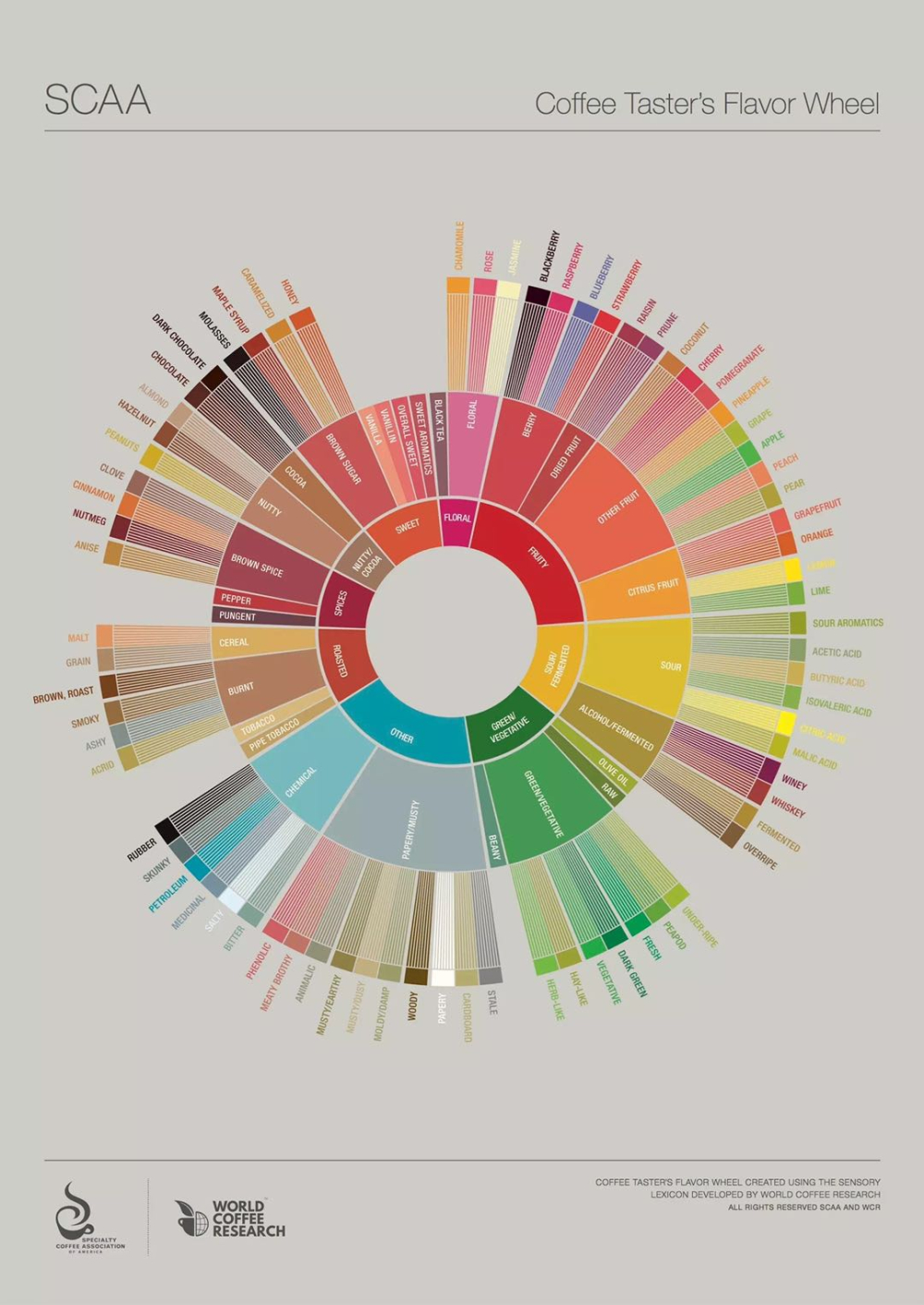
Analysis of the Old Version Flavor Wheel
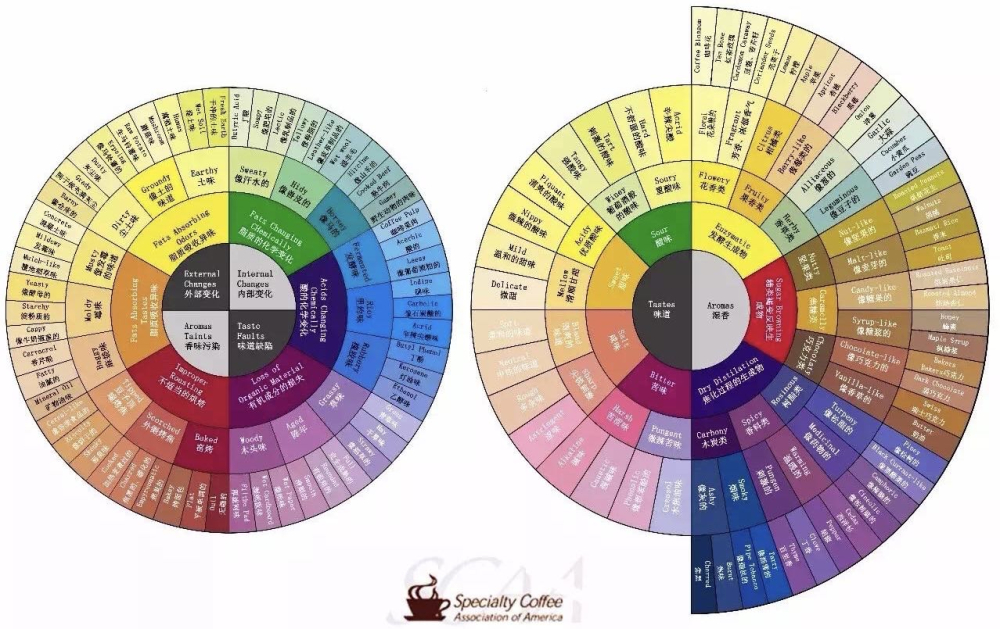
Fans of specialty coffee should be familiar with this SCAA flavor wheel, but many say they don't understand it. Today, let's briefly explain the structure and meaning of the flavor wheel! The flavor wheel is divided into two parts: the negative flavor spectrum on the left and the normal flavor spectrum on the right.
Right Side of the Flavor Spectrum
The Right Half
This section mainly deals with the classification and formation causes of coffee flavors and aromas.
Enzymatic fermentation: This refers to flavors produced during the processing of raw beans (such as washed, natural, honey processed) due to fermentation, such as floral and fruit flavors.
Sugar browning: This part includes flavors produced by caramelization and Maillard reactions during coffee roasting, such as nuts and chocolate.
Dry distillation: This part includes flavors produced by dry distillation reactions during coffee roasting, such as currant and smoky flavors.
Some people claim that "the flavor wheel represents flavors produced by different coffee roasting degrees from top to bottom," but in reality, dry distillation reactions occur from the beginning of roasting, so this statement is not entirely accurate.
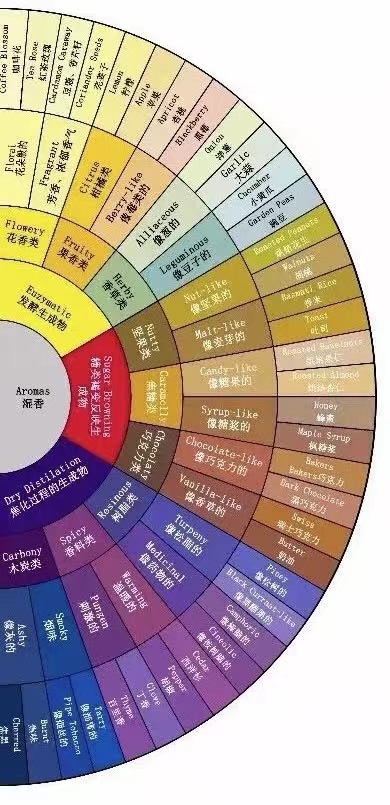
The Left Half
This part is easy to understand - it's the different sensory classifications of basic tastes: sour, sweet, bitter, and salty. It's said that future flavor wheels will include umami.

Left Side of the Flavor Spectrum
Right Half
This section describes defect flavors that arise from improper handling during the harvesting and drying stages, as well as flavors that develop during storage due to aging.
If not processed promptly after harvesting or if drying humidity and temperature are unreasonable, fermentation will produce Rio flavors, fermented flavors, etc. During the drying process, if the temperature is too high and coffee beans heat up too quickly, it will cause fat decomposition, producing leather-like flavors.
During the storage of raw beans after processing is complete, some reactions still occur within the beans. Organic substances gradually change and are lost. New beans will have grassy flavors, and after several years of storage due to organic matter loss, they will develop straw and woody flavors. At this point, the coffee tastes very bland!
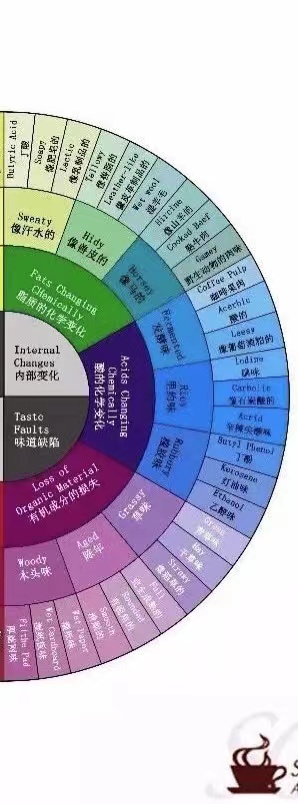
Left Half
This section covers changes caused by external environment (cleanliness, humidity, etc.) during the storage of processed raw beans, as well as flavors produced by whether temperatures are reasonable during the roasting process.
During the processing of raw beans, if the drying environment is not clean - for example, if beans are dried on the ground - the coffee will absorb surrounding odors, producing earthy flavors. Alternatively, if the location has too much humidity, coffee beans dry too slowly and may become moldy, producing musty flavors.
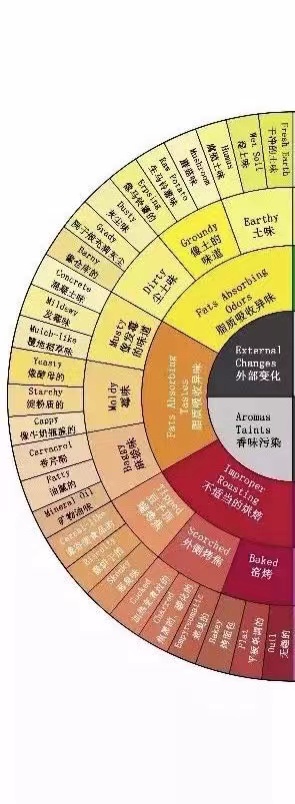
If the temperature rises too quickly during roasting and coffee beans are scorched, it will produce smoky, carbon-like flavors. If the temperature rises too slowly, it will diminish the coffee's flavors, making them seem dull and uninteresting.
On the right side, "fats changing chemically" and "acids changing chemically" produce defect flavors that are considered serious defects. In SCAA cupping, if these flavors are detected, 4 points will be deducted. The defects "fats absorbing odors" and "fats absorbing tastes" on the left are considered minor defects, resulting in a 2-point deduction if detected in cupping. The "improper roasting" and "loss of organic material" categories at the bottom are not considered raw bean defect flavors, so no defect points are deducted, but they will reduce scores in flavor performance.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Coffee Variety Introduction: Pacamara Variety - Blueberry Estate Honey Process Flavor
Pacamara coffee is a hybrid variety discovered in El Salvador in the 1950s, created by crossing Pacas (a natural mutation of Bourbon) with Maragogype (a natural mutation of Typica discovered in Brazil). The coffee tree grows tall with wider branch spacing than Pacas, featuring dark green wavy-edged leaves, and is best cultivated at altitudes of 900-1500 meters.
- Next

Moka Pot Guide: Detailed Explanation of Principles and Proper Usage
The Moka Pot, this classic coffee maker originating from Italy, is extremely popular in its local region. It's said that 8 out of every 10 households own this excellent coffee brewing device. However, in China, the use of Moka Pots is relatively rare, leading many people to lack comprehensive guidance on its usage. Today, FrontStreet Coffee
Related
- How to make bubble ice American so that it will not spill over? Share 5 tips for making bubbly coffee! How to make cold extract sparkling coffee? Do I have to add espresso to bubbly coffee?
- Can a mocha pot make lattes? How to mix the ratio of milk and coffee in a mocha pot? How to make Australian white coffee in a mocha pot? How to make mocha pot milk coffee the strongest?
- How long is the best time to brew hand-brewed coffee? What should I do after 2 minutes of making coffee by hand and not filtering it? How long is it normal to brew coffee by hand?
- 30 years ago, public toilets were renovated into coffee shops?! Multiple responses: The store will not open
- Well-known tea brands have been exposed to the closure of many stores?!
- Cold Brew, Iced Drip, Iced Americano, Iced Japanese Coffee: Do You Really Understand the Difference?
- Differences Between Cold Drip and Cold Brew Coffee: Cold Drip vs Americano, and Iced Coffee Varieties Introduction
- Cold Brew Coffee Preparation Methods, Extraction Ratios, Flavor Characteristics, and Coffee Bean Recommendations
- The Unique Characteristics of Cold Brew Coffee Flavor Is Cold Brew Better Than Hot Coffee What Are the Differences
- The Difference Between Cold Drip and Cold Brew Coffee Is Cold Drip True Black Coffee

