The Development History of Vietnamese Coffee, Flavor Characteristics of Coffee Varieties in Vietnamese Regions, and Introduction to Classic Italian Blends

Vietnam is located at the southeastern end of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia, bordering China, Laos, and Cambodia, with the South China Sea to its southeast. The country features a long, narrow terrain that is roughly S-shaped. The terrain is higher in the northwest and lower in the southeast, with three-quarters of the country consisting of mountains and plateaus. The Truong Son Range runs through the central part of the country from north to south. Vietnam is situated south of the Tropic of Cancer and belongs to the tropical monsoon climate zone. The north experiences four distinct seasons, with average temperatures ranging from 23°C to 25°C in most areas. The south is divided into a rainy season (May to September) and a dry season (October to April), with average temperatures ranging from 26°C to 27°C in most areas. The national average rainfall is 1500-2000 millimeters.
Coffee was introduced to Vietnam by the French in 1867, initially cultivated in plantation models until it reached commercial scale in 1910. Coffee cultivation was interrupted during the Vietnam War, and after the war ended, the coffee industry began to form conglomerates. During this period, approximately 20,000 hectares of land produced 5,000-7,000 tons of coffee. In the following 25 years, the land used for coffee cultivation increased 25-fold, while the total national production grew 100 times. This growth rate can be attributed to the 1986 reform and opening-up policy that allowed private enterprises to produce commercial crops.

By the early 1990s, numerous new companies emerged in Vietnam, many focusing on large-scale coffee production. Particularly between 1994-1998, when coffee prices were high, the Vietnamese industry concentrated on increasing production. By 1996-2000, Vietnam's coffee production had increased significantly, having a major impact on global prices. Vietnam became the world's second-largest coffee producer, leading to global oversupply and causing coffee prices to collapse. However, today's coffee market faces supply shortages, and Vietnam is planning to add new coffee planting areas.
Because the initial focus was on coffee production, the local industry valued quantity over quality. Therefore, Vietnam predominantly produces Robusta, with only some regions cultivating Arabica. The main growing regions are divided into three major areas: the Central Highlands, Southern Vietnam, and Northern Vietnam.
Central Highlands
The Central Highlands consist of a series of plateaus, including provinces such as Dak Lak, Lam Dong, Gia Lai, and Kon Tum. This region primarily cultivates Robusta (Xanh Lun) and some Arabica, producing about 70% of the country's Robusta. The cultivation altitude ranges from 600-1000 meters, with harvesting occurring from November to March of the following year.

Southern Vietnam
Coffee is grown in the areas around Dong Nai Province, northeast of Ho Chi Minh City, also primarily cultivating Robusta TR series. This region has attracted many large coffee companies, such as Nestlé, which has established factories here. The altitude here ranges from 200-800 meters, with harvesting occurring from November to March of the following year.
Northern Vietnam
Arabica is mainly cultivated in places like Son La, Thanh Hoa, and Quang Tri in northern Vietnam, near Hanoi City. This region has higher altitudes that allow Arabica to grow, with elevations between 800-1600 meters. Harvesting also occurs from November to March, primarily cultivating Bourbon, Catimor, and Robusta TR series. Although Arabica only accounts for 3%-5% of Vietnam's total coffee production, it still makes Vietnam the world's fifteenth-largest Arabica producer, which demonstrates Vietnam's high production volume.

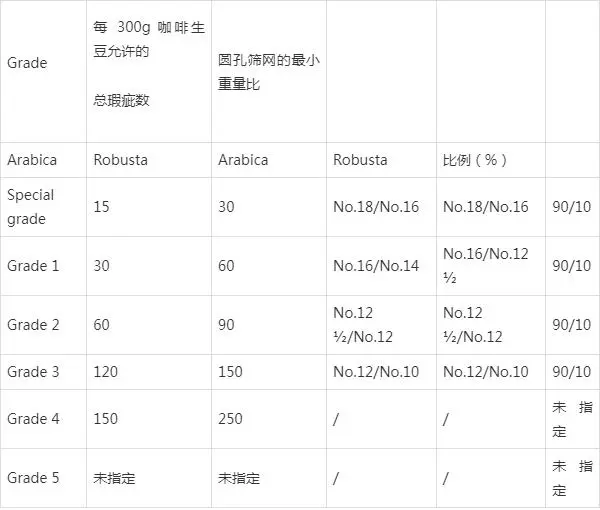
Vietnam's coffee grading system is relatively simple, based on the number of defects in 300g of green coffee beans.
FrontStreet Coffee's classic Italian blend also selects coffee beans produced in Vietnam, using Indonesian Mandheling, Brazilian Cerrado, and Vietnamese Robusta beans for blending. The medium-dark roast presents rich espresso flavors with chocolate and nutty notes, and when paired with milk, it enhances the sweetness.

For professional coffee knowledge exchange and more coffee bean information, please follow Coffee Workshop (WeChat official account: cafe_style).
For more specialty coffee beans, please add FrontStreet Coffee on private WeChat, ID: qjcoffeex
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

The Correct Way to Hold and Move for Latte Art Pours: How to Practice for Better Designs
Many coffee enthusiasts experience this frustrating situation: no matter how you move your pitcher, the latte art patterns and lines simply won't form, or when they do, they appear rather rough and unrefined! Yet others can create delicate patterns with seemingly effortless movements. At this point, many begin to wonder if it's a problem with their "hands," but actually,
- Next

What is the Flavor of White Flowers in Coffee? How to Brew Floral Notes in Pour-Over Coffee?
When purchasing coffee beans, we often find enticing floral descriptions on some packaging. We might impulsively buy them based on these descriptions. However, after brewing and tasting, we frequently find ourselves wondering: "Where are the floral notes? Why can't I taste them?"
Related
- How to make bubble ice American so that it will not spill over? Share 5 tips for making bubbly coffee! How to make cold extract sparkling coffee? Do I have to add espresso to bubbly coffee?
- Can a mocha pot make lattes? How to mix the ratio of milk and coffee in a mocha pot? How to make Australian white coffee in a mocha pot? How to make mocha pot milk coffee the strongest?
- How long is the best time to brew hand-brewed coffee? What should I do after 2 minutes of making coffee by hand and not filtering it? How long is it normal to brew coffee by hand?
- 30 years ago, public toilets were renovated into coffee shops?! Multiple responses: The store will not open
- Well-known tea brands have been exposed to the closure of many stores?!
- Cold Brew, Iced Drip, Iced Americano, Iced Japanese Coffee: Do You Really Understand the Difference?
- Differences Between Cold Drip and Cold Brew Coffee: Cold Drip vs Americano, and Iced Coffee Varieties Introduction
- Cold Brew Coffee Preparation Methods, Extraction Ratios, Flavor Characteristics, and Coffee Bean Recommendations
- The Unique Characteristics of Cold Brew Coffee Flavor Is Cold Brew Better Than Hot Coffee What Are the Differences
- The Difference Between Cold Drip and Cold Brew Coffee Is Cold Drip True Black Coffee

