Introduction to Starbucks Decaf Coffee Flavor and Differences Between Decaf and Regular Coffee

One of the benefits of coffee lies in its caffeine content, which provides an energizing effect. Supplementing with caffeine is one of the reasons many people drink coffee daily. However, everyone's sensitivity to caffeine varies. Some people are highly sensitive to caffeine but still want to enjoy coffee. Are there coffee options with lower caffeine content? Perhaps decaffeinated coffee might be the best choice for those who wish to avoid excessive caffeine intake.
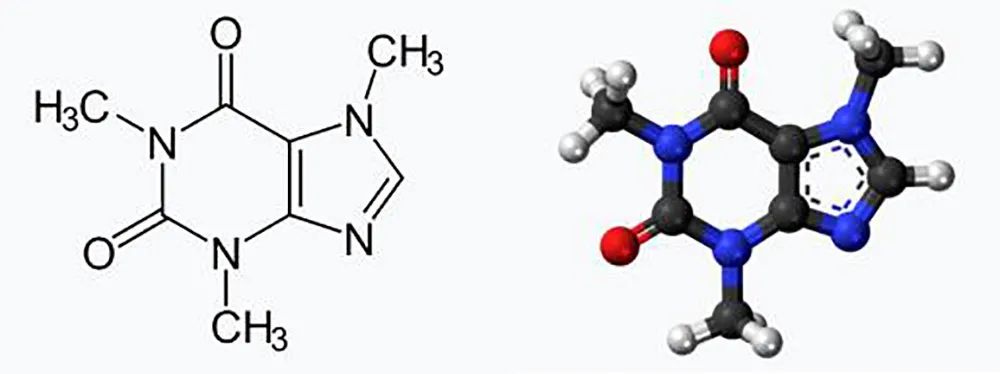
What is Decaffeinated Coffee?
Under normal circumstances, the caffeine content in coffee beans is measured using weight ratios. Arabica coffee beans contain 0.9%-1.4% caffeine (averaging 1.2%), while Robusta beans contain 1.8%-4% (averaging 2.2%). Decaffeinated coffee is divided into naturally low-caffeine coffee and artificially processed decaffeinated coffee.
The most common naturally low-caffeine coffee is Laurina (Coffea Laurina), which contains half the caffeine of regular Arabica beans (0.6%). Unlike other artificially processed decaffeinated coffees, Laurina's lower caffeine content is due to genetic degeneration, resulting in lower caffeine levels compared to typical Arabica coffee trees, with superior flavor.

For artificially processed decaffeinated coffee, the European Union standard requires that the caffeine content after processing does not exceed 0.1% of the raw beans, while the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) standard requires reduction to less than 3% of the original caffeine content.
What are the Decaffeination Processing Methods?
Today, there are many methods for removing caffeine, which can be broadly categorized into direct/indirect solvent processing, supercritical carbon dioxide processing, Swiss water processing, and mountain spring water processing.
Direct Solvent Processing Method
The direct solvent processing method uses chemical solutions such as dichloromethane and ethyl acetate to dissolve caffeine. First, steam opens the pores of the raw coffee beans, then dichloromethane solvent is added directly to the beans. After the solvent combines with the caffeine, the caffeine-rich solvent is washed away, and the beans are steamed again to remove all residual solvent.

Due to concerns that long-term exposure to dichloromethane may increase cancer risk, its use as a solvent raises some concerns. However, the FDA limits the dichloromethane content in decaffeinated coffee to 0.001%, which is actually lower in practice, making side effects minimal.
The process using ethyl acetate as a solvent is the same. Ethyl acetate typically comes from sugarcane, so when used, the direct solvent method is sometimes called the sugarcane decaffeination method. Colombian decaffeination processing typically uses this method. However, ethyl acetate is a highly flammable substance, making it more dangerous.
Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Processing Method
This processing method first allows the coffee beans to absorb water and swell, putting caffeine molecules in a loose state within the beans. Liquefied carbon dioxide is added and creates pressure greater than 100 atmospheres in water. Carbon dioxide is highly selective, dissolving caffeine without "harming" the carbohydrates and proteins in the coffee beans, ensuring that the coffee's flavor is not destroyed. The liquid carbon dioxide that carries away the caffeine can be reused after caffeine removal.

Coffee decaffeinated using carbon dioxide places less burden on the human body, and according to research, this method extracts more caffeine than the direct solvent method, although it costs significantly more than the direct solvent method.
Swiss Water Processing Method
The Swiss Water processing method was developed by the Swiss company Coffex in the late 1970s, and SWISS WATER is now a registered trademark. This processing method soaks raw coffee beans in hot water, during which phase some caffeine is already partially removed. The soaked solution is then filtered through activated carbon, and finally, the solution is returned to the coffee beans. This series of steps more effectively removes caffeine. Besides not requiring chemical solvents, the soaked solution can be reused in different batches of processing, but the coffee still loses some flavor during the filtration process.
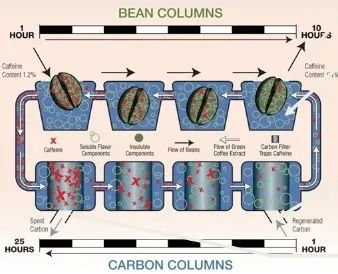
This method can achieve a caffeine removal rate of 99.9%, making it the method with the highest caffeine removal rate. FrontStreet Coffee conducted cupping tests on multiple decaffeinated coffee beans and selected a Colombian Swiss water-processed bean last year. This coffee bean comes from Colombia's Huila region and includes varieties of Typica, Caturra, and Castillo. Combined with the Swiss water processing method, this decaffeinated coffee bean showed distinct notes of dark cocoa, caramel, nuts, and a rich, mellow mouthfeel during cupping.
Mountain Spring Water Processing Method
Similar to Swiss water processing, this method uses another special water—glacier water—to extract caffeine. The company Descamex states that they use a special filtration device to remove caffeine. After processing, a water-based solution without caffeine is obtained, which also dissolves coffee solids and can be reused in the decaffeination process.

Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Why Use 9 Bar for Espresso? How Does Pressure Affect Espresso?
Professional coffee knowledge exchange For more coffee bean information Please follow Coffee Workshop (WeChat public account cafe_style) The key to making espresso lies in pressure, and the crema, volume, and flavor of espresso all come from the effects of pressure. But why is pressure so important? How does it affect the espresso formula? Why is nine atmospheric pressure the most commonly recommended brewing pressure setting
- Next

Introduction to Yirgacheffe Alamo Cooperative: What are the Flavor Characteristics of Yirgacheffe Coffee?
For more professional coffee knowledge and coffee bean information, please follow Coffee Workshop (WeChat official account: cafe_style). Ethiopia, an ancient country on the African continent, is the homeland of Arabica coffee. It is in the forests of Ethiopia's Kaffa region that you can find wild Arabica coffee.
Related
- How to make bubble ice American so that it will not spill over? Share 5 tips for making bubbly coffee! How to make cold extract sparkling coffee? Do I have to add espresso to bubbly coffee?
- Can a mocha pot make lattes? How to mix the ratio of milk and coffee in a mocha pot? How to make Australian white coffee in a mocha pot? How to make mocha pot milk coffee the strongest?
- How long is the best time to brew hand-brewed coffee? What should I do after 2 minutes of making coffee by hand and not filtering it? How long is it normal to brew coffee by hand?
- 30 years ago, public toilets were renovated into coffee shops?! Multiple responses: The store will not open
- Well-known tea brands have been exposed to the closure of many stores?!
- Cold Brew, Iced Drip, Iced Americano, Iced Japanese Coffee: Do You Really Understand the Difference?
- Differences Between Cold Drip and Cold Brew Coffee: Cold Drip vs Americano, and Iced Coffee Varieties Introduction
- Cold Brew Coffee Preparation Methods, Extraction Ratios, Flavor Characteristics, and Coffee Bean Recommendations
- The Unique Characteristics of Cold Brew Coffee Flavor Is Cold Brew Better Than Hot Coffee What Are the Differences
- The Difference Between Cold Drip and Cold Brew Coffee Is Cold Drip True Black Coffee

